Research News
Physiological function of low molecular weight G protein Arf6 in tumor vascularization
The growth of tumor requires oxygen and nutrients provided from blood. So, cancer cells induce the development of "tumor blood vessels" from existing blood vessels to tumors through capillary vessels by releasing various factors to induce blood vessels. That means, suppressing the development of tumor blood vessels can inhibit tumor growth. Many kinds of medicines have been researched to suppress the development of tumor blood vessels. However, the inhibitors of developing tumor blood vessels in clinical use do not show the ideal effect. It is highly expected to find more effective anti-cancer drug.
The research group of Professor Yasunori Kaneyasu, Assistant Professor Tsunaki Hongu and Assistant Professor Yuji Funakoshi of Faculty of Medicine at the University of Tsukuba, by collaboration with the National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center and other research institutes, discovered the critical role of Arf6, low molecular weight G protein, in the development of tumor blood vessels and tumor growth. They found the result by the analysis with the genetically modified mouse.
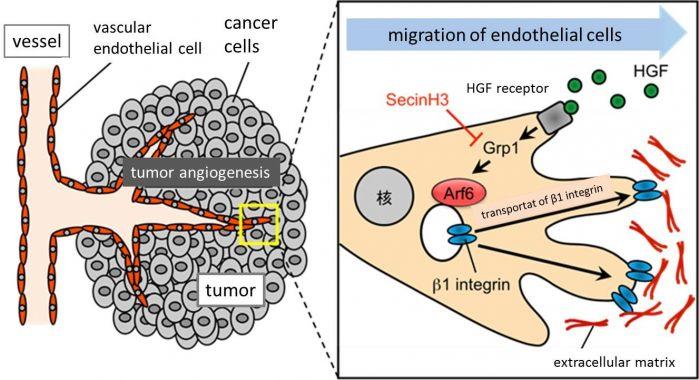
The research group focused on the low molecular weight G protein called Arf6. The protein suppresses the cell vesicular transportation and cell mobility. According to the analysis of the mouse without Arf6 gene located inside of vascular endothelial cells, Arf6 has an important role for the development of tumor blood vessels. The research group also found that Arf6 regulates the development of tumor blood vessels induced by Hepatocyte Growth Factor (HGF) from the secretion of cancer cells. Moreover, around the downstream of HGF signal there is a protein called Grp1 to activate Arf6. The researchers clarified that the activated Arf6 makes the development of tumor blood vessels by suppressing the transportation of b1 integrin, cell adhesion molecule, into the cell membranes. The discovery above means that cell signaling related to Arf6 can be a new target of drug R&D as an inhibitor of tumor blood vessels, which would lead to develop an effective anti-cancer drug.
Original Paper
Tsunaki Hongu, Yuji Funakoshi, Shigetomo Fukuhara, Teruhiko Suzuki, Susumu Sakimoto, Nobuyuki Takakura, Masatsugu Ema, Satoru Takahashi, Susumu Itoh, Mitsuyasu Kato, Hiroshi Hasegawa, Naoki Mochizuki, and Yasunori Kanaho, Nature Communications, Arf6 regulates tumor angiogenesis and growth through HGF-induced endothelial b1 integrin recycling. Doi:10.1038/ncomms8925


