Research News
Measurement of Skeletal Muscle Mass Using the Bioelectrical Impedance Technic in Athletes
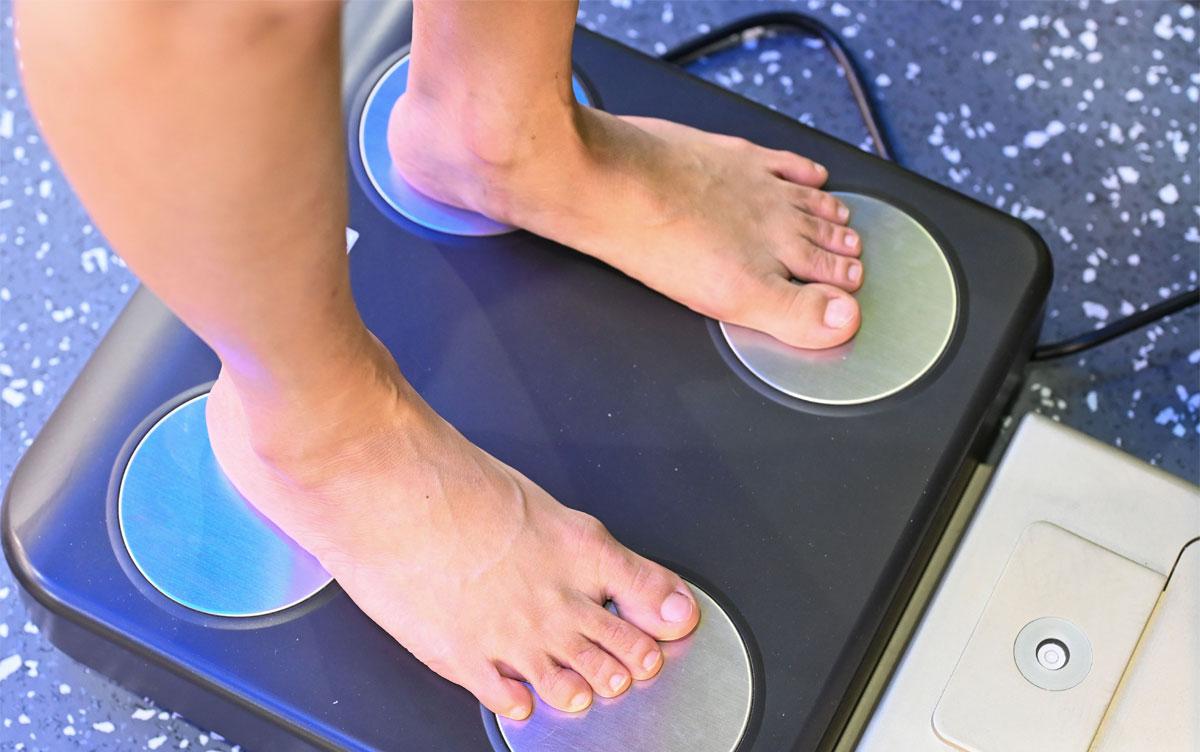
Bioelectrical impedance analysis is a noninvasive and rapid method for estimating body composition, including body fat and muscle mass. Previous studies have indicated that bioelectrical impedance can accurately estimate skeletal muscle mass and intracellular water, even in athletes who possess muscle qualities distinct from the general adult population.
Tsukuba, Japan—Bioelectrical impedance analysis is a method used for estimating body composition. This method estimates body composition based on the degree of current flow in the body, allowing noninvasive and rapid measurement, and is used in home-use body composition monitors and other devices. However, existing estimation methods might not be sufficient for accurately assessing skeletal muscle mass in individuals such as athletes and active men, whose muscle quality and composition differ from those of the general adult population.
In this study, researchers from the University of Tsukuba evaluated the validity of bioelectrical impedance for estimating skeletal muscle mass specifically in athletes and active men. Results revealed a strong correlation between skeletal muscle mass and bioelectrical impedance indices, confirming that bioelectrical impedance is a useful tool for this purpose.
In addition, bioelectrical impedance is effective for estimating intracellular water levels. This finding is likely to encourage broader adoption of bioelectrical impedance for body composition assessments in medical institutions and fitness facilities, making evaluations easier and more accurate. In the future, researchers anticipate the development of more precise estimation formulas, which will facilitate the evaluation of the effectiveness of training and nutritional interventions for athletes. Moreover, the adaptability of these new formulas for diverse populations will be further investigated.
###
This work was supported by the JSPS KAKENHI for HS (16J11877and 20K19563), HT (19H04017), YY (18H03164), the University of Tsukuba Advanced Research Initiative for Human High Performance (ARIHHP), and Casio Science Pro-motion Foundation.
Original Paper
- Title of original paper:
- Comparison of bioelectrical impedance indices for skeletal muscle mass and intracellular water measurements of physically active young men and athletes
- Journal:
- Journal of Nutrition
- DOI:
- 10.1016/j.tjnut.2023.07.010
Correspondence
Assistant Professor SAGAYAMA Hiroyuki
Institute of Health and Sport Sciences, University of Tsukuba
Related Link
Institute of Health and Sport Sciences



